How GPS works?
Computer Network
A computer network is a group of computer systems and other computing hardware devices that are linked together through communication channels to facilitate communication and resource-sharing among a wide range of users.
Advantages of Network
- Facilitate communication via email, video conferencing, instant messaging, etc.
- Enable multiple users to share a single hardware device like a printer or scanner
- Enable file sharing across the network
- Allow for the sharing of software or operating programs on remote systems
- Make information easier to access and maintain among network users
Disadvantages
- Data and information maybe stolen by computer hackers.
- If any computer in the network get affected by the virus, there is high chance of spreading computer virus.
- Computers on the network have to depend on the server.
Communication Media/Channel
Communication media refers to the means of delivering and receiving data or information. In telecommunication, these means are transmission and storage tools or channels for data storage and transmission.
There are two main types of communication channels:
A. Guided or Bounded or Wired Communication Media
B. Unbounded or Unguided or Wireless Communication Media
Guided Media
- A transmission media where data signals are transmitted along a specific path through cable is known as Guided Transmission Media.
- It transfer data from one place to another with the help of wire.
- There are three types of cables used for wired network.
- Twisted Pair Cable
- Co-axial cable
- Fiber optic cable
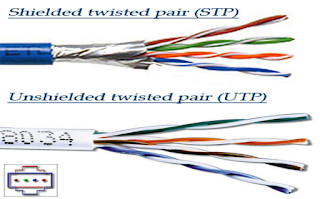
Twisted Pair Wire
- it is used for almost all business telephone wiring
- it consists of strands of copper wire twisted in pair
- it is inexpensive, easy to work and it can be made relatively unobtrusive by running it inside walls, doors or ceilings
- it is relatively slow for data transmission
- it is susceptible to interference from other electrical sources
- it can be easily tapped for gaining unauthorized access
Co-axial Cable
- it consists of insulated copper wire
- it is less susceptible to electrical interference
- it more expensive and less exile than twisted pair
- data transmission over coaxial cable is divided in to two basic types :Base band: transmission is analog and each wire carries only one signal at a time Broadband: transmission is digital and each wire carries multiple signal at time
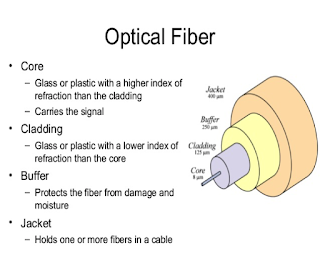
Fiber Optic Cable
- Fiber optic cables are made up of plastic or glass fibers and gives high quality transmission of signal at a very high speed.
- It transmits light rather than electronic signals.
- Fiber optic cable transmission are not affected by electromagnetic interference.
- These can be used to communicate either analog or digital signals.
- These are most commonly used for point to point one way communication.
- It can transmit data at much higher rate than twisted pair and coaxial cable.
- It can carry more data at very high speed and to long distances.
- No sign cant loss of intensity of light, so repeaters need not be placed so closer together as in coaxial cable.
- Transmissions are not affected by electrical and magnetic interference.
- Smaller in size and lighter in weight than others.
- Provides security as it is difficult to tap optical signals.
- Optical fibers are fragile and can't be bend.
- Joining two optical fiber cables is not simple and easy
Unguided Media/Wireless Channel
- The way to transfer data without the help of wire is called Unguided media.
- The type of Communication media in which communication devices sends and receives data signals through air or space is called Unguided media.
- The data is communicated in the form of wave.
- Unguided media provides means to transmit data signals but does not guide them along a specific path.
- The data signals are not bounded to a cabling media.
- Therefore, unguided media is also called Unbounded media.
- The type of Communication media in which communication devices sends and receives data signals through air or space is called Unguided media.
- The data is communicated in the form of wave.
- Unguided media provides means to transmit data signals but does not guide them along a specific path.
- The data signals are not bounded to a cabling media.
- Therefore, unguided media is also called Unbounded media.
Types of unguided media are as follows:
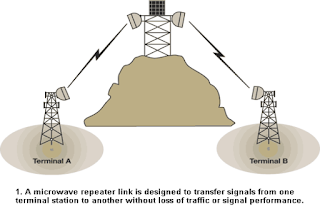
Microwave
- In microwave transmission, data is transmitted through air or space,instead of through cables or wires.
- Microwaves are high frequency radio waves.
- Microwave uses line-of-sight transmission through space.
- Microwave works in LOS (Line of Sight)
- The line-of-sight means that data signals (or waves) can only travel in straight lines and cannot bend.
- The data is transmitted and received through a microwave station.
- A microwave station is also called relay station or booster.
- A microwave station contains an antenna, transmitter, receiver, and other equipment that are required for microwave transmission.
- Microwave antennas are placed on the high towers or buildings.
- These are placed within 20 to 30 miles of each other. there may be many microwave stations between the sender and receiver.
- data is transmitted from one microwave station to another.
- Each microwave station receives signals from previous microwave station and transmits to next station.
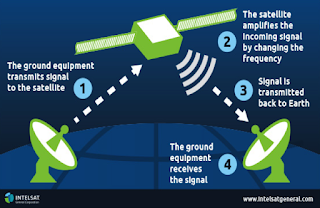
Satellite
- Satellite communication system consists of a satellite and several earth stations.
- The communication satellite is a space station.
- Each earth station consists of large dish antenna. It can send and receive data signals.
- A satellite receives microwave signals (or messages) from earth station.
- It amplify es the signals and sends them to another earth station.
- Data transmission speed of satellite is fast.
- There are generally three types of satellite : GEO (Geo Stationary Orbit), MEO (Medium Earth Orbit), LEO (Lower Earth Orbit)
- Advantage: The main advantage of satellite communication system is that a large amount of data can be communicated from one country to another.
- Disadvantage: The disadvantage of satellite communication is that bad weather can affect the quality of satellite transmission.
Global Positioning System
- The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based navigation system made up of a network of 24 satellites placed into orbit by the U.S. Department of Defense.
- GPS was originally intended for military applications
- in the 1980s, the government made the system available for civilian use.
- GPS works in any weather conditions, anywhere in the world, 24 hours a day.
- There are no subscription fees or setup charges to use GPS.
How GPS Works:
GPS satellites circle the earth twice a day in a very precise orbit and transmit signal information to earth. GPS receivers take this information and use transliteration to calculate the user's exact location.
Essentially, the GPS receiver compares the time a signal was transmitted by a satellite with the time it was received. The time difference tells the GPS receiver how far away the satellite is. Now, with distance measurements from a few more satellites, the receiver can determine the user's position
and display it on the unit's electronic map. A GPS receiver must be locked on to the signal of at least 3 satellites to calculate a 2-D position (latitude and longitude) and track movement. With four or more satellites in view, the receiver can determine the user's 3-D position (latitude, longitude and altitude). Once the user's position has been determined, the GPS unit can calculate other information, such as speed, bearing, track, trip distance, distance to destination, sunrise and sunset time and more.
Radio wave:
A very low frequency electromagnetic wave (from roughly 30 kilohertz to 100 gigahertz). Radio waves are used for the transmission of radio and television signals; the microwaves used in radar and microwave ovens are also radio waves. Many celestial objects, such as pulsars, emit radio waves.
CHECK THIS ALSO:⇊⇊


Comments
Post a Comment